Background
Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project (ADSP)
The Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project (ADSP) is a National Institutes of Health (NIH) and National Institute on Aging (NIA) initiative responding to the National Alzheimer’s Project Act (NAPA) to fight Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). Announced in February 2012, the project is sequencing and analyzing genomes of a large number of well-characterized individuals in order to identify a broad range of AD risk and protective gene variants. The ultimate goal is to facilitate the identification of new pathways for therapeutic approaches and prevention. Analysis of sequences will also provide insight as to why individuals with known risk factor genes escape from developing AD. The overarching goals of the ADSP are to: (1) identify new genomic variants contributing to increased risk of developing Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease (LOAD), (2) identify new genomic variants contributing to protection against developing Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), (3) provide insight as to why individuals with known risk factor variants escape from developing AD, and (4) examine these factors in multi-ethnic populations as applicable in order to identify new pathways for disease prevention.
For more information about the sequence phases go to the ADSP Study page on the NIAGADS DSS website.
Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA)
Cognitive Systems Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease Genetic and Phenotypic Data
https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PAR-19-269.html
Please contact the program officer (Marilyn Miller) regarding RFA and inform National Institute on Aging of your interest in applying. The funding mechanism uses the U01 cooperative research mechanism and the RFA REQUIRES each investigator to notify NIA before applying. Note the earliest due date for grant submission is October 5, 2019 and we urge you to start the process as early as possible to make sure you do not miss any deadlines toward the due date.
Applications that exceed $500K Direct costs in any one year of a potential award must seek pre-approval for submission from NIA AT LEAST 6 WEEKS in advance of submission. Please contact Dr. Miller at millerm@nia.nih.gov to request information on how to provide the appropriate information to NIA.
Data
ADSP Sequencing Phases Completed, In Progress, and Planned:
The following table summarizes samples sequenced or will be sequenced by ADSP, or sequence data from other studies that will be included into the ADSP data collection. ADSP is ongoing and the table is subject to change.
| ADSP Phase | DX | Ethnicity | Gender | Genetic Data | Availability | |||||||
| Case | Control | Other | Non-Hispanic White | African American/ African | Hispanic | Male | Female | GWAS | WGS | WES | ||
| Discovery Case/Control | 5871 | 4805 | 233 | 10578 | 0 | 331 | 4581 | 6328 | 10909 | 0 | 10909 | Anticipate release early 2020 |
| Discovery + Extension Family Based | 540 | 286 | 21 | 386 | 29 | 432 | 310 | 537 | 847 | 847 | 0 | Available through DSS |
| Extension Case/Control | 1437 | 1658 | 0 | 979 | 981 | 1135 | 1060 | 2035 | 3095 | 3095 | 0 | Available through DSS |
| FUS 1 | 5503 | 10300 | 0 | 2872 | 6466 | 6465 | na | na | 15803 | 15803 | 0 | Anticipate release mid-2020 |
| FUS 2 | 1403 | 5802 | 2011 | 8199 | 1017 | 0 | na | na | 9216 | 9216 | 0 | Anticipate release mid-2021 |
| FUS 3 | 3320 | 1787 | 0 | 4107 | 500 | 500 | na | na | 5107 | 5107 | 0 | Anticipate release mid-2022 |
| Total | 18074 | 24638 | 2265 | 27121 | 8993 | 8863 | 5951 | 8900 | 44977 | 34068 | 10909 | |
| *content in italics are planned |
View table in full screen
ADSP Study Design and Selection Criteria
The following two documents outline the study design and sample selection criteria.
- Discovery Phase: Beecham et al. The Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project: Study design and sample selection. Neurology Genetics. 2017.
- Discovery Extension Phase: Discovery Extension Sample Selection Criteria
Access ADSP data
Qualified investigators can request access to ADSP data through the NIAGADS Data Sharing Service (DSS) website. To review instructions on how to apply for data, please go to the DSS Application Instructions page.
What is available now?
The first dataset includes Compressed Sequence Alignment files (CRAMs) mapped to GRCh38 and GATK-called gVCFs from the ADSP and ADNI studies. These data were called by the Genome Center for Alzheimer’s Disease (GCAD) using the VCPA 1.0 pipeline. Analysis-ready project-level VCF files are generated using GATK joint genotype calling followed by quality control checks developed by GCAD and the ADSP QC workgroup. GCAD processed a total of 4,789 whole genomes, including 876 samples from the ADSP Family Discovery and Discovery Extension phase, 3,104 samples from the ADSP Case Control Extension phase, and 809 samples from the ADNI study.
For more information please visit DSS datasets page.
What will we have in the next few years?
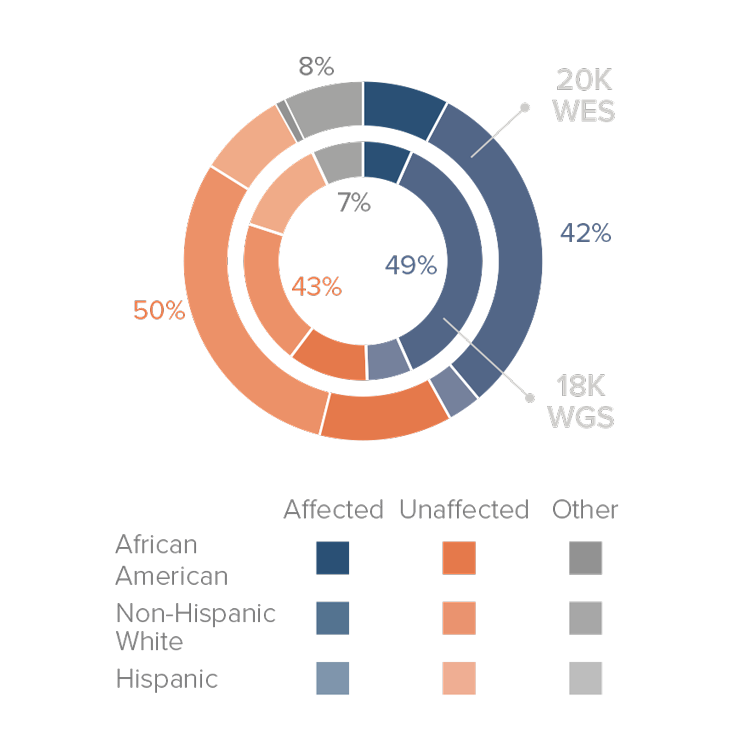
The current ADSP Follow-Up Sequencing (FUS) phase will sequence additional samples with focus on diversity and well-characterized cohorts. Between Fall 2019 and Spring 2020, ADSP will release sequence and joint call genotyping data of >20,000 whole exomes and >18,000 whole genomes (including the 4,789 genomes released in 2018). GCAD plans to have one major release each year which includes cumulative joint calls combining previously released genomes and new genomes. The table at the beginning of the Data section outlines the planned data releases and timeline.
Available Phenotypes
All sequencing data releases include basic phenotypes including Diagnosis, Age (at onset / last visit / at death), Sex, APOE genotype (e2/e3/e4 alleles), Race/Ethnicity. Please refer to Data Dictionary Files listed below for the minimal set of phenotypes collected for the GCAD harmonized whole-genome/exome datasets:
Many of the studies in ADSP collect additional clinical data about the participants. NIAGADS works with these cohorts and domain experts to identify relevant clinical data and process them into harmonized phenotypic data that can be analyzed together, with focus on the following five categories:
- cognitive tests
- neuropsychiatric symptoms
- cardiovascular risk factors
- imaging biomarkers
- fluid biomarkers
NIAGADS will provide updates on additional phenotypic data availability and harmonization procedure as they become available.
Other genomic data resources
The following Excel spreadsheet lists studies and sources with genomic data relevant to the scientific objectives of ADSP. Some of these datasets are publicly available, and some other datasets are managed by their respective data custodians and cannot be shared directly by NIAGADS. To access these datasets, please visit the study websites and follow their instructions.
Platform for data access
The NIAGADS Data Sharing Service (DSS) is a repository that facilitates the deposition and sharing of genomic data from the ADSP and other NIA funded Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias genomic studies with approved users in the research community.
Principal investigators can request DSS distributed data through the Data Access Request Management (DARM) system by logging in using their eRA Commons ID. Once an application is approved by the NIAGADS ADRD Data Access Committee (NADAC) and Data Use Committee (DUC), the data can be accessed through the Data Portal and downloaded directly or through Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2).
Follow the links below to learn more about DSS.
https://dss.niagads.org/
https://dss.niagads.org/documentation/
How to participate
NIAGADS is the designated data coordinating center to support the Cognitive Systems Analysis initiative. To apply for funding under this RFA, investigators please do the following:
- Please contact the program officer (Marilyn Miller) regarding RFA and inform NIA of your interest in applying. The funding mechanism uses the U01 cooperative research mechanism and the RFA REQUIRES each investigator to notify NIA before applying. Note the earliest due date for grant submission is October 5, 2019 and we urge you to start the process as early as possible to make sure you do not miss any deadlines toward the due date.
- Apply for access to the data collection through NIAGADS DSS so you will have access to the data. ADSP data are from human subjects and require a proper application and review process.
- To ensure integrity of the grant application and peer review process, please direct all questions regarding the RFA to the program officer, not NIAGADS. The program officer will review the questions and forward to NIAGADS if NIAGADS needs to be consulted.
- See the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) page regarding the initiative. Someone else might have already asked your questions and you can find answers there.
You do not have to be a funded investigator to access data or contribute to the overall analysis effort. If you have any non-RFA questions regarding data availability and available resources, feel free to contact NIAGADS directly. Our mission in supporting this RFA is to facilitate community analysis of the data resources and redistribute analysis results and tools developed by the community, and we look forward to working with everyone.
FAQ
What is the size estimate of the raw sequencing data?
Whole-genome CRAMs are ~30Gb and gVCFs are about 5-10Gb per sample.
Whole-exome CRAMs are ~5Gb and gVCFs are about 1.5Gb per sample.
What is the computing cost for downloading the data?
The costs associated with downloading are dependent on whether you are downloading to another AWS resource or outside AWS. You would not be charged if you download within the same region as our S3 bucket, US-East (N. Virginia), to another US-East (N. Virginia) AWS resource. Generally it would cost $0.09 per GB download to download to resources outside of AWS. See the pricing table for specifics: S3 Data Transfer Pricing.
If you plan to download the data locally, an affordable transfer option is an Amazon Snowball (more details below). The device costs $250 to transfer 80TB of data. See the pricing information for specifics: Amazon Snowball Pricing.
For CRAMs and gVCFs, the requesting institution will incur the cost of downloading the data. These files can be downloaded using the Amazon Requester Pays option. Downloading genotype, phenotype, and miscellaneous files are free to the requesting institution.
What is the computing cost for analyzing the data?
As analysis strategies and needs vary from one team to another, NIAGADS does not cover cost of computing activities by individual investigators and their teams. Investigators who plan to analyze the data on the cloud will cover the computing expenses for their own computing activities, including use of instances and storage, data egress from data storage or archive services, or any other services by the cloud providers. We recommend the investigators to acquire expertise in cloud computing management, talk with NIAGADS to learn about how NIAGADS shares data on the clouds, and develop an estimate of computing costs, and include in their budgets when submitting applications for the RFA.
What does NIAGADS charge for the service?
NIAGADS does not charge for the service if all the investigators want is to access data.
When will the 20,000/30,000/50,000 genomes be available?
Please see the table in the Data section regarding sample and availability timeline.
What phenotypic data is available?
All sequenced samples come with basic phenotypic data such as diagnosis, sex, age. Many of the cohorts in ADSP have additional clinical data such as fluid biomarkers, cognitive tests, and imaging. NIAGADS is working with the cohorts and domain experts to collect and harmonize these data. See the Data section for more information.